Australia’s education system is highly regarded globally, making it a popular destination for international students. The system is structured into several levels, providing diverse opportunities for learners from primary education to higher education. Other big factors behind Australian universities being consistently ranked in the QS World Ranking and Times Higher Education Rankings are academic performance, campus life, and trained instructors. It has a well-structured program that emphasizes diverse capacities, such as critical thought, imagination, communication, comprehension, capacity for logical reasoning, ethical awareness, and more.

Structure of the Education System
The Australian education system is primarily divided into four main levels:
- Primary Education: Covers grades from Prep (kindergarten) to Year 6.
- Secondary Education: Encompasses Years 7 to 12, culminating in the Senior Secondary Certificate of Education.
- Vocational Education and Training (VET): Focuses on practical skills and industry training, offered through institutions like TAFE (Technical and Further Education).
- Higher Education: Includes universities that provide undergraduate and postgraduate degrees.
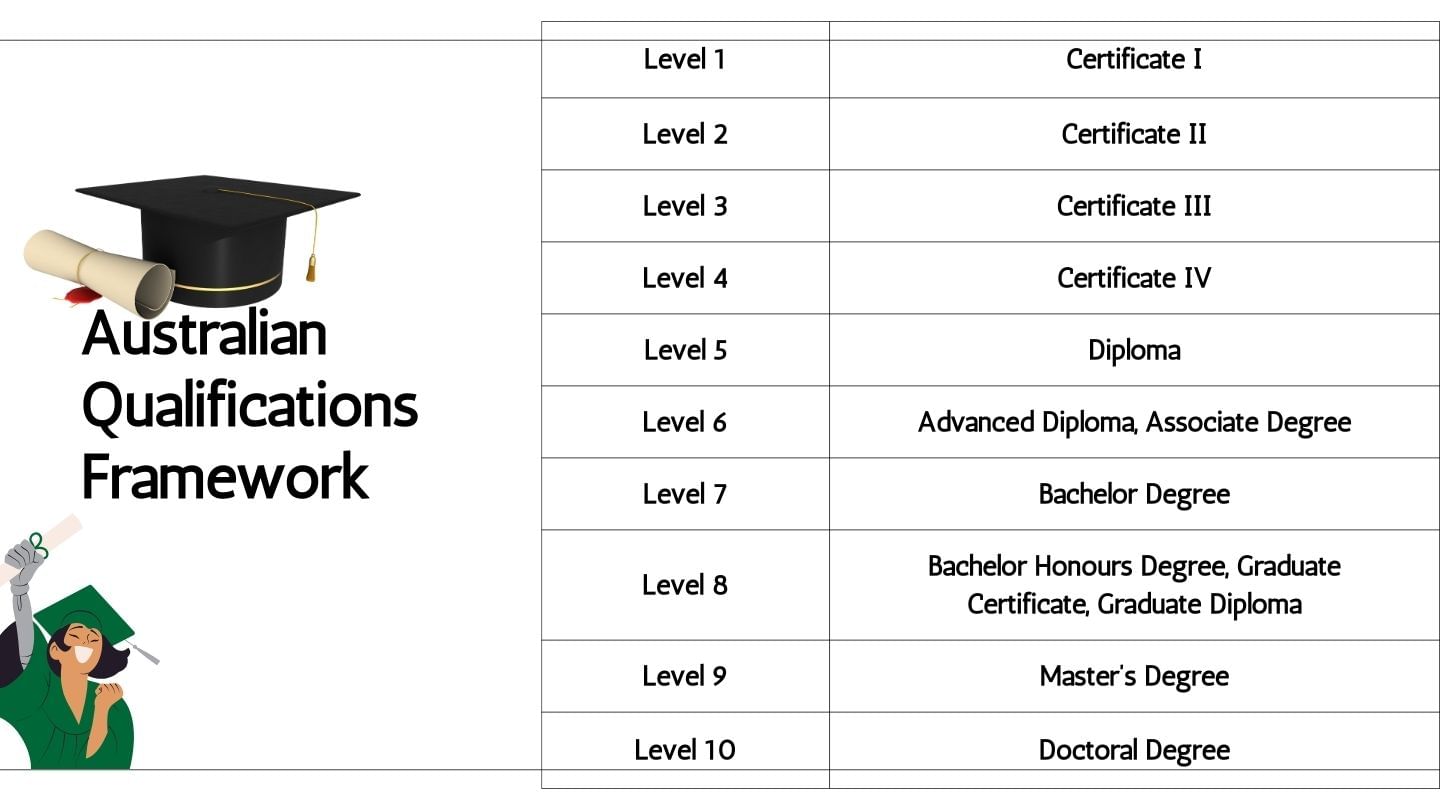
Australian Qualifications Framework (AQF)
Established in 1995, the AQF regulates all educational qualifications in Australia, ensuring consistency and high standards across institutions. It consists of ten levels, ranging from Certificate I to Doctoral Degrees, which helps international students understand the equivalency of their qualifications.
Enrollment and Application Process
International students must enroll in institutions registered on the Commonwealth Register of Institutions and Courses for Overseas Students (CRICOS). This registration ensures that the institution meets specific quality standards and provides protections such as the Tuition Protection Service (TPS) for students.
Benefits Of Studying In Australia
Australia offers a wealth of benefits to international students, making it a top destination for education. From academic excellence to multicultural diversity and promising career opportunities, the advantages of studying in Australia are immense.
Academic Excellence
Australia is renowned for its world-class education system and high-quality universities. With seven institutions consistently ranked among the top 100 globally, students receive education that meets rigorous international standards. Australian universities also prioritize research and innovation, offering extensive opportunities to contribute to advancements in fields like technology, medical science, and environmental sustainability.
Diverse Learning Environments
Australia’s education system emphasizes a holistic approach to learning, combining theoretical knowledge with practical application. Small class sizes foster a more interactive learning environment, enabling students to actively engage with peers and instructors. This dynamic approach ensures that students graduate with not only academic qualifications but also practical skills tailored to industry demands.
Global Networking Opportunities
Studying in Australia provides unparalleled opportunities to build a global network. International students interact with peers from diverse cultural and professional backgrounds, enriching their perspectives and experiences. Many universities have strong ties with industries, offering internships and work placements that connect students with professionals in their chosen fields. These connections often pave the way for valuable career opportunities post-graduation.

Support for International Students
Australia is dedicated to ensuring the well-being of its international student community. Universities offer robust support systems, including academic mentoring, mental health counseling, and career guidance services. Additionally, cultural adaptation programs help students settle into their new environment, making the transition smoother and more enjoyable. Orientation sessions, student clubs, and community engagement activities further contribute to a supportive and inclusive atmosphere.
Post-Study Opportunities
Australia’s policies are highly favorable to international graduates. The Temporary Graduate Visa (subclass 485) allows students to remain in the country after completing their studies, gaining valuable work experience. Many courses align with Australia’s Skilled Occupation List (SOL), increasing the chances of securing permanent residency. These opportunities make Australia an attractive destination for those looking to establish a career and life abroad.
By combining high-quality education, supportive environments, and global opportunities, Australia offers a truly enriching experience for international students. Whether your goals are academic, professional, or personal, Australia provides the tools and pathways to achieve success.
Costs and Scholarships
The costs associated with studying in Australia include tuition fees, living expenses, and additional costs like health insurance and travel. Below is a breakdown:
| Expense | Approximate Cost (AUD) |
| Undergraduate Tuition | 20,000 – 45,000 per year |
| Postgraduate Tuition | 22,000 – 50,000 per year |
| Vocational Courses (VET) | 4,000 – 22,000 per year |
| Living Expenses | 21,041 per year (as per visa requirement) |
| OSHC (Health Insurance) | 450 – 600 per year |
| Public Transport & Misc. | 30 – 60 per week |
Scholarships for International Students
Australia offers a variety of scholarships to reduce the financial burden for international students:
| Scholarship Name | Details |
| Australia Awards | Fully-funded scholarship covering tuition, travel, and living expenses. |
| Destination Australia Scholarship | Up to AUD 15,000 per year for students studying in regional areas. |
| University-Specific Scholarships | Examples include ANU Chancellor’s International Scholarship and Melbourne International Undergraduate Scholarship. |
| Research Training Program (RTP) | Funding for research-based postgraduate degrees. |
| Commonwealth Scholarships | Support for students from Commonwealth countries. |
Tips to Secure Scholarships
- Start your application process early and prepare a strong statement of purpose.
- Demonstrate academic excellence and leadership skills.
- Research institution-specific grants and regional scholarships.
Student Life and Support Services
Australia offers a vibrant student life with numerous opportunities for cultural exchange and networking. Major cities like Melbourne and Sydney are known for their high quality of life and student satisfaction. Educational institutions provide various support services, including academic counseling, language assistance, and career advice.
Post-Graduation Opportunities
International students who complete their studies in Australia can benefit from post-study work rights through the Temporary Graduate visa (subclass 485). This allows graduates to gain practical experience in their field of study while residing in Australia.
The education system in Australia is designed to be inclusive and supportive of international students. With a focus on practical skills, high academic standards, and a strong regulatory framework through the AQF and CRICOS, Australia remains a top choice for those seeking quality education abroad.
FAQs
Is education free in Australia for International students?
Education is not free for international students in Australia. They typically pay tuition fees, which can range from AUD $20,000 to AUD $30,000 per year, depending on the course and institution. However, scholarships are available that can cover tuition and living expenses for eligible students.
Is the education system in Australia good?
Yes, the education system in Australia is considered to be very good, consistently ranking among the top in the world for quality and standards. It offers a comprehensive curriculum, highly qualified teachers, and a wide range of internationally recognized qualifications.
What is level 1,2,3 university in Australia?
In Australia, universities are often categorized into levels based on their prestige and academic performance. While level 1 means high-ranked and top performing universities, 2 means they have a good reputation but not as great as level 1, and level 3 focuses more on vocational training and applied learning.
What is the study pattern in Australia?
The study pattern in Australia typically involves a structured approach with two main semesters per academic year. The first semester usually starts in late February or early March and runs until late May or early June, while the second semester begins in late July or early August and concludes in November.
What syllabus is followed in Australia?
Australia follows a national curriculum known as the Australian Curriculum, which is implemented in primary and secondary schools across the country. It includes core learning areas such as English, Mathematics, Science, and Humanities, among others, and is designed to ensure consistent education standards regardless of the state or territory.
We hope you enjoyed reading this blog on The Education System in Australia. Don’t forget to read some of our other blogs like –
- 15 Best Australian Festivals You Can’t Afford To Miss
- Australian Student Visa Process: The Easy Guide
- Bet You Didn’t Know About These 8 Breathtaking Beaches In Australia















0 Comments